Video of the Week:
Making Your Own Seed Tape
Vegetables:
Cure the Itch by Planting Peas

Recommended varieties include Dwarf Grey Sugar and Mammoth Melting Sugar. Sugar snap peas resemble shelling peas but have a thick, fleshy pod and can be eaten fresh, steamed or cooked. Like snow peas, they are not shelled but eaten pod and all. We recommend Sugar Bon, Sugar Ann, Super Sugar Snap and Sugar Sprint.
Peas should be planted shallow, about one-half inch deep, to encourage rapid germination and emergence. Seed in the row should be spaced 2 inches apart. Many people often plant two rows 6 to 8 inches apart so the floppy plants can support one another. For some older varieties, this may not be enough. They may need trellising to support the growing vines. Fencing may be needed to keep rabbits away. (Ward Upham)
Lettuce

Seed should be started four to five weeks before transplanting. Because transplants are placed at the same time as direct seeding, now would be a good time to begin. Use a seed starting mix and plant shallow as lettuce requires light for germination. A soil media temperature of 60 to 68 degrees will encourage germination. Watch the media temperature carefully, as seed can enter a thermal dormancy if germination temperatures are excessive. Also, a cooler temperature of 55 to 60 degrees should be used once the plants emerge.
Time to maturity varies depending on the type of lettuce, with leaf lettuce being the quickest, followed by bibb, romaine, and buttercrunch lettuce. Head or crisphead lettuce is the slowest and is least likely to mature before becoming bitter.
Spacing also varies with type. Leaf lettuce plants are spaced 4 to 6 inches apart, buttercrunch, bibb, and romaine are set at 6 to 8 inches and head lettuce should be at least 8 inches apart in the row. Lettuce does not have an extensive root system and requires regular watering if rainfall is lacking.
Fertilize before planting according to soil test. Plants should also be sidedressed when about 1/3 grown. Sidedressing is done with fertilizers that have more nitrogen than phosphorus and potassium. Use 1/3 cup of nitrate of soda (16-0-0) or 1/4 cup of a 27-3-3, 29-5-4 or similar fertilizer per 10 feet of row. The latter fertilizers are lawn fertilizers but will work well for sidedressing as long as they do not contain weed killers or weed preventers. (Ward Upham)
Soil Temperature and Vegetables

A number of vegetables can germinate and grow at cool temperatures. For example, peas will germinate and grow well at a soil temperature of 40 F. Though lettuce, parsnips, and spinach can sprout at a soil temperature of 35 F, they prefer at least 45 F for best germination and growth. Radishes also do well at a soil temperature of 45 F. Warm-season crops such as tomatoes, sweet corn and beans prefer at least 55 F for germination (or transplanting), but others such as peppers, cucumbers, melons and sweet potatoes need it even warmer, about 60 F.
Taking soil temperature accurately is a bit of a science. First, use a metal soil thermometer, which is sold in many garden, auto parts and hardware stores. Take temperature 2.5 inches deep at about 10 to 11 a.m. Temperature variations throughout the day and night affect soil temperature, with lowest readings after dawn and warmest around mid-afternoon. The late-morning reading gives a good average temperature. If taking the soil temperature at this time is not practical, take a reading before you leave for work and a second when you return home and use the average. Also be sure to get a consistent reading for four to five days in a row before planting, and make sure a cold snap is not predicted.
An excellent guide sheet on this subject is published by the Alabama Cooperative Extension System and is titled “Soil Temperature Conditions for Vegetable Seed Germination.” It can be found at http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR-1061/ANR-1061.pdf (Ward Upham)
Ornamentals:
Forcing Stems of Woody Plants for Indoor Blooms

Remember that the flower buds on forsythia are killed as temperatures reach –10 degrees F. If your area has had temperatures this far below zero, use one of the other woody plants.
Choose a day that is above freezing for collecting branches for blooming. Keep the stem length to 3 feet or less. As you cut, place the stems in a bucket of water. Once you have the number of branches you want, bring them into the house and soak them in warm water for several hours -- a bathtub works well for this. This ensures that the stems and buds are fully hydrated. Next, place them in a container that has a warm, preservative solution and place them in an environment with high humidity and plenty of light.
Make your preservative solution by dissolving packets of floral preservative in water. These packets can often be obtained from your local florist. You can also make your own preservative by adding a tablespoon of Listerine per gallon of water, but commercial preservatives are preferred. Floral preservatives accomplish two functions; they prevent bacterial growth in your water and provide nutrients and energy for the life processes of the plants.
Many times our houses have a very low relative humidity during the winter. These low humidities can lead to dehydration of flower buds and blossoms. To raise the humidity around your plants, mist the plants or drape a dry cleaner's bag over your stems. If a cleaner's bag is too small, use a painter’s clear plastic drop cloth. Humidifiers can also help raise humidity levels. Normally, forsythia will take about nine days to flower, quince will require between 12 to 20, and pussywillow needs from five to 15 days. The time required will vary depending on indoor conditions and how late in the winter the branches were collected. Most woody plants should be in flower within three weeks of collection and will remain in flower for about a week before blooms start to fade. (Ward Upham)
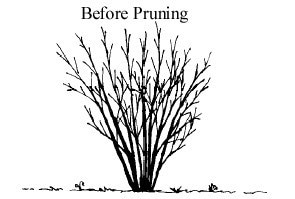
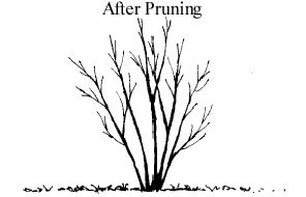
Pruning Deciduous Shrubs
Deciduous shrubs are placed into three groups:
- Those that flower in the spring on wood produced last year;
- Those that flower later in the year on current seasons’ growth; and
- Those that may produce flowers, but those flowers are of little ornamental value.
Shrubs that flower in the spring should not be pruned until immediately after flowering. Though pruning earlier will not harm the health of the plant, the flowering display will be reduced. Examples of these types of plants include forsythia, lilac and mock orange. Shrubs that bloom on current seasons’ growth or that do not produce ornamental flowers are best pruned in late winter to early spring. Examples include Rose-of-Sharon, pyracantha, Bumald spirea and Japanese spirea.
Pruning during the spring allows wounds to heal quickly without threat from insects or disease. There is no need to treat pruning cuts with paints or sealers. In fact, some of these products may retard healing. There are three basic methods used in pruning shrubs: thinning, heading back and rejuvenating. Thinning is used to thin out branches from a shrub that is too dense. It is accomplished by removing most of the inward growing twigs by either cutting them back to a larger branch or cutting them back to just above an outward- facing bud. On multi-stemmed shrubs, the oldest canes may be completely removed.
Heading back is done by removing the end of a branch by cutting it back to a bud and is used for either reducing height or keeping a shrub compact. Branches are not cut back to a uniform height because this results in a "witches-broom" effect.
Rejuvenation is the most severe type of pruning and may be used on multi-stem shrubs that have become too large, with too many old branches to justify saving the younger canes. All stems are cut back to 3- to 5-inch stubs. This is not recommended for all shrubs but does work well for spirea, forsythia, pyracantha, ninebark, Russian almond, little leaf mock orange, shrub roses and flowering quince. (Ward Upham)
Miscellaneous:
An Easy Way to Propagate Houseplants

Prepare the Cutting
- Remove about a 4-inch or smaller piece from the tip of the plant. The cut should be made just below a node. A node is where a leaf attaches to the stem.
- Remove the leaf or leaves from the bottom node. This is where roots will form.
- If there are just a few leaves on the tip, fine. However, if there is a cluster of leaves, remove most of them below the tip. This will cut down on water loss as the plant makes new roots.
Plant the Cutting
- Push the bottom end of the cutting into the soil. The remaining leaves should not contact the soil. A rooting hormone may be used if desired but usually is unnecessary with houseplants.
Make a Greenhouse
- Place 3 straws equidistant from each other near the outside edge the cup full of potting soil. They will support the plastic bag so that it does not contact the leaves and cause them to rot.
- Place the plastic bag over the cup like a tent and use the rubber band to secure the open end of the bag to the sides of the cup.
Grow the Cutting
- Place the cutting in bright, indirect light. Do not place in full sunlight as the cutting may overheat.
- Keep the cutting warm. A temperature of 72 degrees is ideal. Roots should form in about 10 days. Check by removing the plastic bag and pulling gently on the cutting. If it doesn’t pull out easily, roots have started to form and the plastic bag can be left off. (Ward Upham)
Leaching Houseplants

Fertilizers are salts. They must be salts in order for the plant roots to take them up. However, salt levels can build up over time and eventually may harm plant roots leading to scorched leaves and unhealthy plants. Though this can happen under field conditions, especially in low rainfall areas, it is particularly critical with houseplants.
Houseplants have a certain soil volume that doesn’t change until a plant is repotted. Salt build-up can be a crucial concern especially if plants are fertilized heavily. Leaching an overabundance of salts can be an important practice to ensure the health of our houseplants. Leaching is not a complicated or difficult process. It consists of adding enough water to wash out excess salts.
How much water is enough? Add the amount of water that would equal twice the volume of the pot. This, of course, would need to be done outside or in a bathtub or sink. Water must be added slowly so that it doesn’t overflow the rim of the pot. If salt has formed a crust on the surface of the soil, remove it but don’t take more than 1/4 inch of the underlying media. This may also be a good time to repot the plant. (Ward Upham)
Contributors: Ward Upham, Extension









 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
