 Garden catalogs seem to come earlier each year. Since new seed can be expensive, you may want to consider using seed bought in previous years. We normally consider seed will remain viable for about 3 years under cool, dark, dry, conditions though there are exceptions. For example, members of the carrot family (carrots, parsnips and parsley) are short-lived and are usually good for only 1 to 2 years. Colorado State University has a publication giving more detailed information on the longevity of specific species at https://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/yard-garden/storing-vegetable-and-flower-seeds-7-221/ . If you are unsure of viability and have plenty of seed, there is an easy method of determining how good your seed is. Place 10 seeds on a paper towel moistened with warm water and cover with a second moistened towel. Roll up the towels and place inside a plastic bag with enough holes for air exchange but not so many that the towels dry quickly. Place the bag in a warm place such as the top of a refrigerator. Remoisten towels with warm water as needed. After the first week, check for germination. Remove sprouted seed and check again after another week. Add these numbers together to determine the percent germination. (Ward Upham)  Be on the lookout for mouse tunnels around your fruit plants. Trunks and roots of apple trees are among the favorite meals for mice. There is probably no damage yet. But if we receive enough snow to cover winter food supplies, mice will begin to feed on the lower area of tree trunks and roots. This feeding may be severe enough to girdle tree trunks and kill the trees. Mice like to hide in dead grass and weeds around the trees, especially close to the trunks. They will often tunnel near the soil surface and feed on the tree bark. You can check for mice by placing baited mouse traps in PVC or other pipe near your trees. Insert the traps far enough so that pets are unable to reach the trap. Check the stations about once a week and reset traps if necessary. Mouse damage can be severe enough to kill trees that are old enough to bear fruit. Clear dead grass and weeds away from your trees and monitor for mice if you are using mulch around your fruit plants. (Ward Upham)  Though trees are a vital part of our landscapes, there are situations where volunteer trees need to be controlled. This is often a case of the wrong plant in the wrong place. If the tree is still small and a desirable species, you may want to consider transplanting in the spring. If it is not, active control measures would be in order. Most, but not all, trees resprout after cutting. Cutting those that don't resprout is an effective control method. For example, eastern redcedar is a very common species that will not resprout after cutting. Those that do resprout include Siberian elm, hackberry, Osage orange (hedgeball), oak, ash, aspen, cottonwood, maple, sycamore, willow and many more. These trees will either need to be dug out or the cut stump treated with herbicide after cutting. Note that when we say volunteer trees, we mean those that come from seed rather than suckers that originate from the roots of an existing tree. The recommendations given in the remainder of this article are designed to kill these volunteer trees. Using herbicides on suckers will damage and very possibly kill the original tree. Trees that commonly produce suckers include tree of heaven, honeylocust, black locust, hackberry, western soapberry, cottonwood, aspen, poplar, willow and boxelder. It is also possible for larger trees of the same species to be root-grafted. Even though root-grafted trees are not suckers, they do share materials between the individual root systems and therefore herbicides used to treat one tree can be passed to its neighbor. Let's say we have a tree we want to control that is a volunteer and there are no other trees of the same species close enough to be root-grafted that we do not wish to harm. What do we do? If the tree is any size, you probably do not want to dig it out. That leaves using a herbicide on the cut stump. Basal treatments are also possible but that is beyond the scope of this article. First decide what herbicide to use. Triclopyr and glyphosate are the herbicides most commonly available to homeowners. Triclopyr is found in many brush killers and glyphosate is found in Roundup as well as numerous other products. Read the label before purchasing to make sure that a cut stump treatment is listed. Most often the undiluted product or lightly diluted product is applied to the stump immediately after cutting. A paint brush is often used for the application though some people will dip their pruning shears in the products immediately before cutting. Regardless, it is important that the stump is treated immediately or at least within 5 minutes. Note that a paint brush with foam rather than bristles is less likely to drip. Trees do not need to be actively growing to be controlled. Actually this time of year is a very good time to treat as long as applications are made when the temperature is above freezing. (Ward Upham)  Now would be a good time to check the location of foliage houseplants to be sure the plants don't get too cold this fall or winter. Plants next to windows or in entryways near outside doors are at the greatest risk. Plants sensitive to cold temperatures include Chinese evergreen (Algaonema), flamingo flower (Anthurium), croton (Codiaeum), false aralia (Dizygotheca), and ming and balfour aralia (Polyscias). Monitor and maintain temperatures above 65 degrees F for the false aralia and above 60 degrees for the rest of the list. Many other indoor plants prefer temperatures above 50 degrees. If needed, move plants away from the windows or door entrances to reduce cold temperature exposure. It may be necessary to move some plants from windowsills before shades or drapes are pulled, especially in the evening. (Ward Upham) 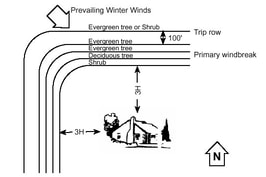 The Kansas Forest Service offers low-cost tree and shrub seedlings for use in conservation plantings. Plants are one to two years old and sizes vary from 8 to 18 inches, depending on species. Two types of seedlings are offered; bareroot and containerized. Containerized provide a higher survival rate and quicker establishment. Orders are accepted from now through May 1st, but order early to ensure receiving the items you want. Orders are shipped beginning in mid-March. Approved uses for these plants include windbreaks, wood lots, wildlife habitat, timber plantations and educational and riparian (streambank) plantings. They may not be used for landscape (ornamental) plantings or grown for resale. All items are sold in units. Each single species unit consists of 25 plants. For example, a unit of Eastern red cedar has 25 trees per unit. Though a single species unit is most commonly purchased, four special bundles are also available including a quail bundle, pheasant bundle, eastern pollinator bundle and western pollinator bundle. Tree planting accessories are also available including marking flags, root protective slurry, rabbit protective tubes, weed barrier fabric and tree tubes. If there have been problems with deer browsing on young trees, the tree tubes are a must. For details and an order form, go to: http://kfs.mybigcommerce.com/. Order forms are also available from local K-State Research and Extension offices. (Ward Upham)  The best time to seed cool-season grasses such as tall fescue and Kentucky bluegrass is September because the turf has more time to mature before spring crabgrass germination and the heat stress of summer. Dormant seeding of turfgrass is sometimes used to help fill in bare spots of lawns that weren't overseeded in the fall. Dormant overseeding is done during the winter (December – February) when it is much too cold for germination. As with any seeding program, good seed-soil contact is vital. Several methods can be used. One method is to seed when there has been a light snowfall of up to an inch. This is shallow enough that bare spots can still be seen. Spread seed by hand on areas that need thickening up. As the snow melts, it brings the seed into good contact with the soil where it will germinate in the spring. Another method is dependent on the surface of the soil being moist followed by freezing weather. As moist soil freezes and thaws, small pockets are formed on the wet, bare soil that is perfect for catching and holding seed. As the soil dries, the pockets collapse and cover the seed. A third method involves core aerating, verticutting or hand raking and broadcasting seed immediately after. Of course, the soil must be dry enough and unfrozen for this to be practical. With any of the above methods, seed germinates in the spring as early as possible. There will be limitations on what herbicides can be used for weed control. Dithiopyr, found in Hi-Yield Turf and Ornamental Weed and Grass Stopper and Bonide Crabgrass & Weed Preventer, can be used on tall fescue, Kentucky bluegrass, and perennial ryegrass two weeks after germination. Other homeowner preemergence herbicides available to homeowners require that the turf be well established before application. (Ward Upham)  People in the eastern third of the state have been reporting shrubs with bright red berries growing wild. The berries are clustered around the stem and the leaves are still a bright green color. These are likely one of two species of bush honeysuckle, (Amur or Tartarian), which can get 6-20 feet tall. This landscape shrub has become a serious understory invasive throughout the midwest from eastern Kansas to Ohio. Many states have it on their noxious weeds list. All of our native honeysuckles are vines, similar to the vining Japanese honeysuckle. Bush honeysuckles are also noticeable in the spring as they put out leaves much earlier than most other trees and shrubs. Leaves also stay green much later into the fall. This long growing season gives it a competitive advantage over other native species, and the vigorous growth can take over a woodland understory, reducing the number of native woodland wildflowers and other shrubs. If you want to promote native species on your property, then controlling bush honeysuckles is needed. Honeysuckle seedlings can be readily hand pulled when the soil is damp. Chemical control is needed for larger infestations, as cutting alone results in vigorous resprouting. Foliar applications of glyphosate (i.e., Roundup) in late summer and fall works well as does applications of Crossbow (2,4-D + triclopyr). Treating cut stumps with concentrated (20% - 50%) glyphosate is also quite effective. Several studies have shown basal spraying with triclopyr (Garlon) not to be effective, while basal applications with 2,4-D or picloram products work well, using an oil carrier to penetrate the bark. Cut stump and basal treatments can be done when the areas to be sprayed are dry and not frozen. Please follow all label instructions when using pesticides. (Charlie Barden and Ward Upham)  Compost piles should be turned about once per month even during the winter months. This will ensure the composting process continues and that all materials are equally composted. A compost pile is “turned’ when uncomposted material is moved from the sides and tops of the pile to the center where it provides “fuel” for the microorganisms that break it down. Water may need to be added if the material you move to the center is dry. Check the moisture content by squeezing a fistful in your hand. It should feel moist but no excess water should drip out. Compress the material in the pile as best you can as excess air can slow the composting process. (Ward Upham) |
AuthorsCynthia Domenghini runs the Horticulture Response Center in the Department of Horticulture and Natural Resources at Kansas State University. Other contributors include K-State Extension Specialists. Archives
March 2024
Categories
All
|
| K-State Research and Extension Horticulture Newsletter |
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
