Video of the Week:
When to Harvest Eggplants
Upcoming Events:

Thursday, August 6, 2015
K-State Research & Extension Center, Olathe
The field day program is designed for all segments of the turf industry - lawn care, athletic fields, golf courses, and grounds maintenance. Included on the program are research presentations, problem diagnosis, commercial exhibitors, and equipment displays. There will be time to see current research, talk to the experts and get answers to your questions.
Pesticide recertification credits in 3A and 3B are available, as well as GCSAA education points.
For more information and to register, go to: https://www.eventbrite.com/e/kansas-turf-ornamentals-field-day-tickets-16109376579
Vegetables:
Common Smut on Sweet Corn

Immature smut galls are considered an edible delicacy known as cuitlacoche in Mexico. They are a high value crop for some growers in the northeast U.S. who sell them to Mexican restaurants. There is no chemical control for this disease. Crop rotation and a balanced fertilizer program can help minimize this disease. Remove and destroy galls from infected plants before they rupture. (Ward Upham)
Blossom-End Rot

- This year, inconsistent amounts of water may be a factor. This can be due to watering practices or may be due to heavy rains followed by dry periods. Try to keep soil moist but not waterlogged. Mulching can help by moderating moisture levels over time.
- Vegetable tops will sometimes outgrow the root system during cooler spring weather. This is especially true of tomatoes. As long as it is cool, the root system can keep up. When it turns hot and dry, the plant has a problem, and water —with the calcium it carries — goes to the leaves and the fruit is bypassed. The plant responds with new root growth and the condition corrects itself after a couple of weeks.
- Heavy fertilization, especially with ammonium forms of nitrogen, can encourage this condition. Heavy fertilization encourages more top than root growth and the ammonium form of nitrogen competes with calcium for uptake.
- Anything that disturbs roots such as hoeing too deeply can encourage blossom-end rot. Mulching helps because it keeps the soil surface cooler and therefore a better environment for root growth.
There are some years you do everything right and the condition still shows up due to the weather. In such cases, remember that blossom-end rot is a temporary condition, and plants should come out of it in a couple of weeks. You may want to pick off affected fruit to encourage new fruit formation.
Soils with adequate calcium will not benefit from adding additional calcium. If your soil is deficient in this nutrient, add 1 pound gypsum per 100 square feet. Gypsum is calcium sulfate and will not affect pH. Though calcium raises pH, sulfate lowers it and the two cancel each other out. Even if not needed, gypsum will not hurt anything.
We have also found that spraying plants with calcium doesn't work. The fruit's waxy surface doesn't allow absorption of the material and calcium does not move from the leaves to the fruit. (Ward Upham)
How to Pick a Ripe Melon

Let’s start with the easy one. Muskmelons are one of those crops that tell you when they are ready to be picked. This can help you not only harvest melons at the correct time but also choose good melons when shopping.
As a melon ripens, a layer of cells around the stem softens so the melon detaches easily from the vine. This is called “slipping” and will leave a dish-shaped scar at the point of stem attachment. When harvesting melons, put a little pressure where the vine attaches to the fruit. If ripe, it will release or “slip.”
When choosing a melon from those that have already been harvested, look for a clean, dish-shaped scar. Also, ripe melons have a pleasant, musky aroma if the melons are at room temperature (not refrigerated).
Watermelons can be more difficult and growers often use several techniques to tell when to harvest.
1. Look for the tendril that attaches at the same point as the melon to dry and turn brown. On some varieties this will need to be completely dried before the watermelon is ripe. On others it will only need to be in the process of turning brown.
2. The surface of a ripening melon develops a surface roughness (sometimes called “sugar bumps”) near the base of the fruit.
3. Ripe watermelons normally develop a yellow color on the “ground spot” when ripe. This is the area of the melon that contacts the ground.
Honeydew melons are the most difficult to tell when they are ripe because they do not “slip” like muskmelons. Actually, there is one variety that does slip called Earlidew, but it is the exception to the rule. Ripe honeydew melons become soft on the flower end of the fruit. The “flower end” is the end opposite where the stem attaches. Also, honeydews should change to a light or yellowish color when ripe, but this varies with variety. (Ward Upham)
Flowers:
Peony "Measles"

Sanitation is the best control for this disease. Remove all diseased tissue, including stems, at the end of the growing season. Mulch that contains plant debris should also be discarded and then replaced with fresh mulch. Reducing the source of the inoculum will reduce the chances of another severe outbreak next year. (Ward Upham)
Pests:
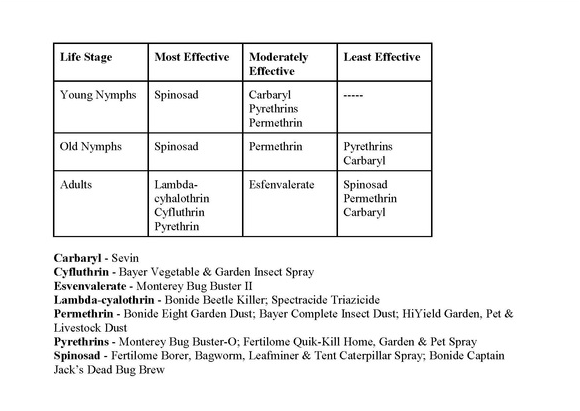
Grasshoppers

We often have gardeners who are interested in organic controls. Nosema locustae, a protozoan, is the active ingredient in a number of products including Semaspore, NOLO Bait, HopperStopper and Grasshopper Attack. These products are selective and will affect only grasshoppers. This is a trait many gardeners find attractive. However, Nosema locustae products may not be as effective in garden situations as they would be under large-scale rangeland conditions due to potential reinfestations from outside the treated area. Also, these products have other potential disadvantages:- They are most effective against nymphal rather than adult grasshoppers. Also some grasshopper species are less susceptible than others.
- Kill can take 3 to 6 weeks after ingestion.
- These baits are perishable and should be kept refrigerated until use. Pay attention to the expiration date.
As mentioned above, reinfestations of uninfected grasshoppers can occur. These products are not effective against adults. Try to treat the nesting area when hoppers are small and populations are concentrated. Nosema locustae products are allowed in certified organic crop production. Poultry including turkeys, guinea hens and chickens have also been used to help control grasshoppers.
Regardless of method used, the trick is to treat early before the population has matured. Young nymphal stages are much easier to control than adults and are also much less mobile. (Ward Upham)
Ornamentals:
Twig Dieback on Oak

Botryosphaeria canker differs from oak wilt in that only the tips of branches are affected. Oak wilt affects whole branches. This disease causes such minor damage that chemical control measures are unwarranted. Dead twigs on small trees may be pruned off if desired. (Ward Upham)
Contributors: Ward Upham, Extension Associate






















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
