Video of the Week:
Self-watering Planter Saves Time
Turfgrass:
Proper Timing for Crabgrass Preventers

Crabgrass preventers are just that – preventers. With few exceptions they have no effect on existing crabgrass plants, so they must be applied before germination. Additionally, preventers do not last forever once applied to the soil.
Microorganisms and natural processes begin to gradually break them down soon after they are applied. If some products are applied too early, they may have lost much of their strength by the time they are needed. Most crabgrass preventers are fairly ineffective after about 60 days, but there is considerable variation among products. (Dimension and Barricade last longer. See below.)
For most of Kansas, crabgrass typically begins to germinate around May 1 or a little later. April 15 is normally a good target date for applying preventer because it gives active ingredients time to evenly disperse in the soil before crabgrass germination starts. However, this year, we may want to go a week or two early. However, for southeast Kansas, this week would be more appropriate, and for northwest Kansas, mid-April would be best.
This year, it may be bet to base timing on the bloom of ornamental plants. The Eastern Redbud tree is a good choice for this purpose. When the trees in your area approach full bloom, apply crabgrass preventer. A follow-up application will be needed about 8 weeks later unless you are using Dimension or Barricade. Products that do require a follow-up application include pendimethalin (Scotts Halts) and Team (Hi-Yield Crabgrass Control).
Dimension and Barricade are the only two products that give season-long control of crabgrass from a single application. In fact, they can be applied much earlier than April 15 and still have sufficient residual strength to last the season. Barricade can even be applied in the fall for crabgrass control the next season.
Dimension can be applied as early as March 1. Because of the added flexibility in timing, these products are favorites of lawn care companies who have many customers to service in the spring. Though Dimension is usually not applied as early as Barricade, it is the herbicide of choice if it must be applied later than recommended. It is the exception to the rule that preemergence herbicides do not kill existing weeds. Dimension can kill crabgrass as long as it is young (two- to three-leaf stage). Dimension is also the best choice if treating a lawn that was planted late last fall. Normally a preemergence herbicide is not recommended unless the lawn has been mowed two to four times. But Dimension is kind to young tall fescue, perennial ryegrass, and Kentucky bluegrass seedlings and some formulations can be applied as early as two weeks after the first sign of germination. However, read the label of the specific product you wish to use to ensure that this use is allowed. Lawns established in the fall can be safely treated with Dimension the following spring even if they have not been mowed.
Note that products containing Dimension and Barricade may use the common name rather than the trade name. The common chemical name for Dimension is dithiopyr and for Barricade is prodiamine. Remember, when using any pesticide, read the label and follow instructions carefully.
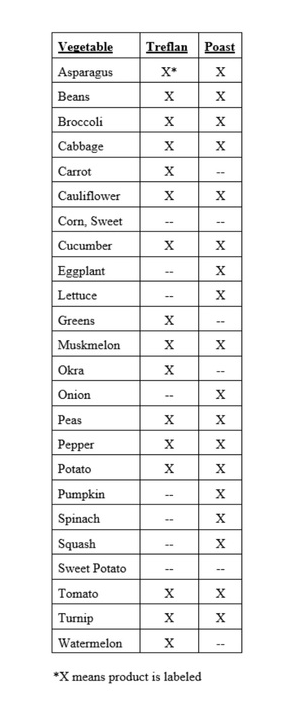
We recommend crabgrass preventers be applied before fertilizer so that the grass isn’t encouraged to put on too much growth too early. However, it may be difficult to find products that contain preemergents without fertilizer. Those that don’t contain fertilizer are listed below. I didn’t find any products containing Barricade that did not also have a fertilizer. If anyone knows of other products that should be listed, let us know and we will publish them in a later newsletter.
Pendimethalin
- Scotts Halts
Team (Benefin + Trifluralin)
- Hi-Yield Crabgrass Control
Dimension
- Hi-Yield Turf & Ornamental Weed and Grass Stopper
- Bonide Crabgrass & Weed Preventer
- Green Light Crabgrass Preventer
(Ward Upham)
How Low Should You Go

Crabgrass seed must have light to germinate, and a high mowing height will help shade the soil. Also, root depth and mowing height are related on upright growing grasses such as tall fescue and Kentucky bluegrass — the higher the height of cut, the deeper the root system. A deeper root system means a more drought-resistant turf.
So, how low should you go on the first cutting? On tall fescue and Kentucky bluegrass, you can mow as low as 1 to 1½ inches. Be careful you don't go so low that you scalp the turf. After that, raise the mowing height for Kentucky bluegrass to 2 to 3 inches but 3 to 3½ inches for tall fescue. (Ward Upham)
Vegetables:
Starting Tomatoes Early

Root Growth: Tomatoes need a soil temperature of at least 55 degrees to do well. Plastic mulch is most commonly used to warm the soil. Several days may be needed to raise the soil temperature. Check the soil temperature 2.5 inches deep in the soil at about 11:00 a.m. If that is not possible, check the temperature before leaving for work and again when your return and use the average of the two. You may wish to lay a drip irrigation line before installing the plastic to make watering more convenient. See accompanying article on laying plastic mulch.
Air Temperature: Plants must be protected from frost. Hot caps or water teepees are placed over the young plants to provide protection as well as a higher average temperature to encourage growth. Eventually the plants will outgrow the cover and start to develop flowers. But if the temperature goes below 55 degrees at night, tomato flowers may not set. The plant is not hurt, but the blossom will not set fruit, or, if it does set fruit, the fruit is often misshapen.
How early can you transplant? Start with a date about 2 weeks earlier than normal. (Ward Upham)
Laying Plastic Mulch

1. Fertilize according to soil test. You won't be able to add fertilizer after the plastic is down.
2. Work the soil so that the bed can be easily shaped.
3. Use a garden hoe to form a trench along all edges of the plastic. The soil should be pulled to the outside of the bed. The trench should be formed six inches in from the edge of the plastic and extend along both sides and both ends. The trench should be deep and wide enough to bury six inches of plastic.
4. Lay trickle irrigation tube down the center of the bed. This isn't absolutely necessary but it makes it much easier to water. Overhead watering will hit the plastic and roll off.
5. Lay the plastic down and cover the edges with soil. You may need to slit the edge of the plastic where the trickle irrigation tube enters the end of the bed.
6. Plant when the soil temperature reaches the correct temperature for the crop (55 degrees for tomatoes and 60 degrees for melons) at a 2.5-inch depth. Check the temperature at about 11:00 a.m. to get a good average temperature. Check for several days in a row to ensure the temperature is stable. (Ward Upham)
Miscellaneous:
Transplant Solutions and Sidedressings

Transplant solutions (root stimulators) are available for sale but it is also possible to make your own transplant solution from a fertilizer that contains more phosphorus than nitrogen or potassium such as a 5-10-5, 10-20-10 or 11-15-11. Mix 2 to 3 tablespoons of one of the above fertilizers in a gallon of water several hours before use. The fertilizer won't completely dissolve but enough will go into solution to get plants off to a good start. Use about 1 cup of transplant
solution for each transplant.
Sidedressing is a fertilization done after the plants are established. A fertilizer containing primarily nitrogen is used to keep plants growing and productive. Nitrate of soda (16-0-0) is often used at the rate of 2 pounds fertilizer per 100 feet of row. More commonly available lawn fertilizers such as a 30-3-3, 29-5-4 or something similar can also be used but cut the rate in half.
Be sure any lawn fertilizer used does not contain weed preventers or weed killers. Note that most fertilizers weigh about 1 pound per pint of product. We have a sidedressing sheet available that lists crops, rate of fertilizer application and timing of application(s) for many common vegetables as well as annual flowers. The sheet can be viewed at http://www.hfrr.ksu.edu/doc1991.ashx (Ward Upham)
Organic Sources of Nitrogen Fertilizer

Product Analysis Pounds/ 100 sq ft Notes
Blood Meal 12-0-0 5 - 10 Can burn plants if overapplied
Cottonseed Meal 6-0.4-1.5 10 May have pesticide carryover
Soybean Meal 7-2-1 8
Feed stores will often sell these products. Colorado State University has an excellent publication on organic fertilizers at http://www.ext.colostate.edu/mg/Gardennotes/234.html (Ward Upham)
Contributors: Ward Upham, Extension Associate
























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
